Quality testing is an essential test item to ensure safe implementation of regenerative medicine.
H.U. Cells performs testing required by ICHQ5A, Q5D, and other regulations for biopharmaceuticals (biotechnology-applied drugs/biologically derived drugs) and regenerative medicine products by biological methods in accordance with the Japanese Pharmacopoeia at SRL, Inc., a member company of H.U. Group.
◎According to the purpose of the test/consignor's request, we perform "1. testing that meets the reliability standards of application materials stipulated in Article 43 of the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act Enforcement Regulations" and "2. other testing."
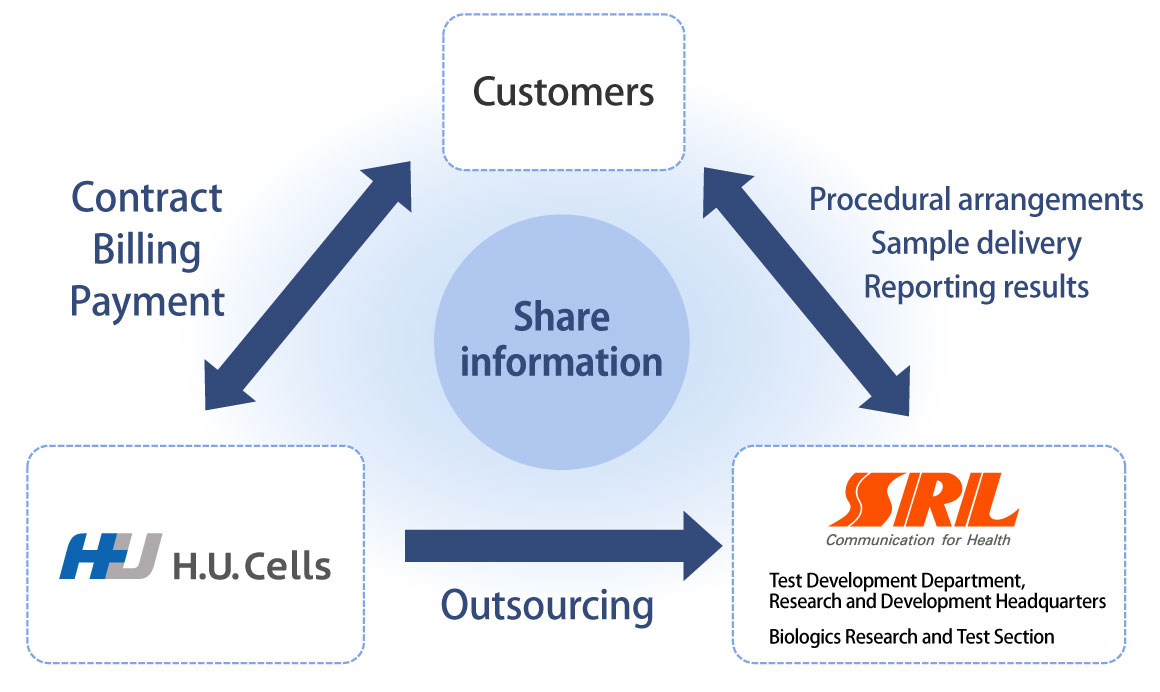
Quality test implementation system
H.U. Cells acts as the contact point and coordinates a meeting with quality test personnel at SRL regarding the test contents.
Subsequently, we prepare an estimate and handle it with the contract.
Quality testing is performed by the Biologics Research and Test Section of SRL, which communicates with customers in a timely manner and performs high-quality testing.
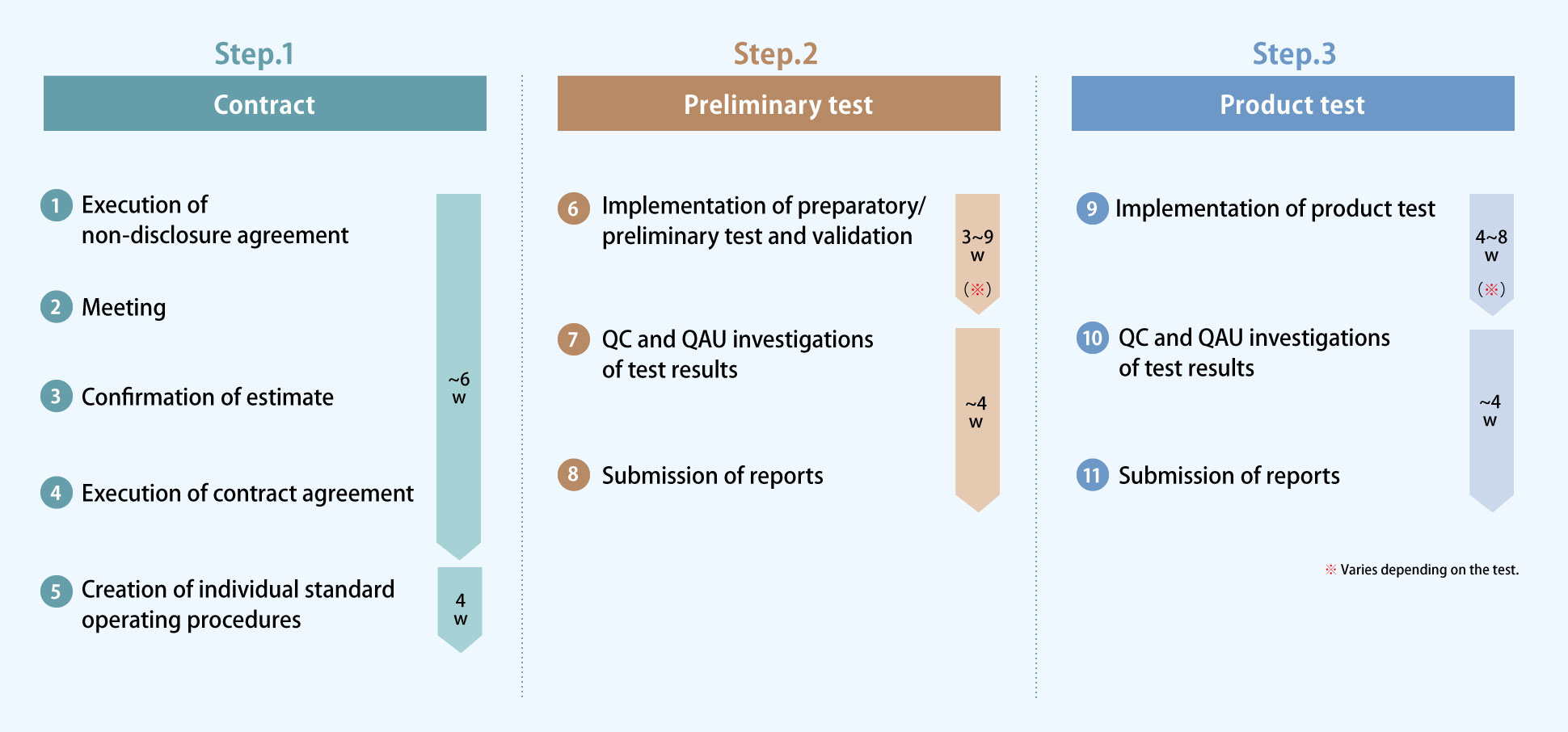
Test flow
The above flow and duration is just an example. It depends on the customer's development situation, the position of the requested test, and other factors.
A standard operating procedure (measurement SOP) will be prepared for each test before it is conducted. The duration will vary depending on the time required for the content.
In accordance with the Japanese Pharmacopoeia, we perform a product test after the preliminary test (validation test).
Bacterial Endotoxins Test


Endotoxin amplifies factors contained in the lysate reagent, and measures gelation, increased turbidity, and yellow coloration due to the cleavage of synthetic substrates by a series of reactions, determining the amount of endotoxins.
We use the turbidimetric method of optical quantification.
Bacterial Endotoxins Test
*1 Backed up samples are included.
*2 This indicates the period of time from the receipt of a sample to the issuance of the reports. An agreement must be signed and a procedure must be prepared in advance.
*3 It should be determined by a test for interfering factors.
Test for interfering factors
We check the provided samples in advance for factors that may interfere with (promote or inhibit) the reaction during the test.
In principle, we conduct a bacterial endotoxins test (for new samples) after a test for interfering factors.
Sterility test


We undertake a sterility test to check for the presence of microorganisms (bacteria or fungi) that can grow using the culture method with the following test methods, in accordance with the Japanese Pharmacopoeia.
-
Direct inoculation
-
Membrane filtration (MF method)
*Growth promotion test: We perform an in-house test in advance for the culture medium used in this test, and consequently, culture medium compliant with sterility and growth promotion tests will be used.
Sterility test
*1 Y is determined by manufacturing scale, standard, and other factors (including backups).
*2 This indicates the period of time from the receipt of a sample to the issuance of the reports. An agreement must be signed and a procedure must be prepared in advance.
Method suitability test
A method suitability test is a method for confirming the presence or absence of antimicrobial activity of the submitted sample (sample or product under test), which is performed prior to or simultaneously with a sterility test.
Sterility test (test for sterility of the product to be examined) is performed using the method examined in the method suitability test.
Sample volume to be tested for sterility
The number of final products to be tested for sterility is defined by the number of units produced per lot.
At the same time, the minimum sample volume per culture medium is determined by the content per vessel of the product.
These two requirements will determine the amount of product to be used for sterility test.
The following table shows the minimum sample volume per culture medium and the minimum number of samples under testing as described in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia.
Minimum sample volume per culture medium
| Product | Content of vessel | Minimum amount to be inoculated into each culture medium, unless otherwise specified |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid | Less than 1mL | Full volume |
| 1mL or more and 40mL or less | Half volume, but not less than 1 mL | |
| More than 40mL and less than 100mL | 20mL | |
| More than 100mL | 10%, but 20mL or more | |
| Liquid antibiotics | 1mL | |
| Water-insoluble drugs, creams or ointments used by being suspended or emulsified | 200mg or more | |
| Solid dosage form | Less than 50 mg | Full volume |
| 50mg or more and less than 300mg | Half volume, but not less than 50mg | |
| 300mg or more and 5g or less | 150mg | |
| more than 5 g | 500mg |
| Content of vessel | Minimum amount to be inoculated into each culture medium, unless otherwise specified |
|---|---|
| Liquid | |
| Less than 1mL | Full volume |
| 1mL or more and 40mL or less | Half volume, but not less than 1 mL |
| More than 40mL and less than 100mL | 20mL |
| More than 100mL | 10%, but 20mL or more |
| Liquid antibiotics | 1mL |
| Water-insoluble drugs, creams or ointments used by being suspended or emulsified | |
| 200mg or more | |
| Solid dosage form | |
| Less than 50mg | Full volume |
| 50mg or more and less than 300mg | Half volume, but not less than 50mg |
| 300mg or more and 5g or less | 150mg |
| More than 5g | 500mg |
Minimum number of samples tested per lot (Minimum number of samples under test)
| Product | Number of units produced per lot (*1) | Minimum number of test samples per culture medium, unless otherwise specified(*2) |
|---|---|---|
| Injectable | 100 vessels or less | 10% or 4 vessels, whichever is greater |
| 101 vessels or more and 500 vessels or less | 10 vessels | |
| 501 vessels or more | 2% or 20 vessels (10 vessels for preparations with an indicated volume of 100 mL or more), whichever is smaller | |
| Parenteral preparations, ophthalmic and other non-injectable preparations (*3) | 200 vessels or less | 5% or 2 vessels, whichever is greater |
| 201 vessels or more | 10 vessels | |
| Solid bulk products | 4 vessels or less | Each vessel |
| 5 vessels or more and 50 vessels or less | 20% or 4 vessels, whichever is greater | |
| 51 vessels or more | 2% or 10 vessels, whichever is greater |
| Number of units produced per lot ((*1) | Minimum number of test samples per culture medium, unless otherwise specified(*2) |
|---|---|
| Injectable | |
| 100 vessels or less | 10% or 4 vessels, whichever is greater |
| 101 vessels or more and 500 vessels or less | 10 vessels |
| 501 vessels or more | 2% or 20 vessels (10 vessels for preparations with an indicated volume of 100 mL or more), whichever is smaller |
| Parenteral preparations, ophthalmic and other non-injectable preparations(*3) | |
| 200 vessels or less | 5% or 2 vessels, whichever is greater |
| 201 vessels or more | 10 vessels |
| Solid bulk products | |
| 4 vessels or less | Each vessel |
| 5 vessels or more and 50 vessels or less | 20% or 4 vessels, whichever is greater |
| 51 vessels or more | 2% or 10 vessels, whichever is greater |
*1 If the number of units produced per lot is unknown, the maximum number shown in this column should be used.
*2 If the contents of one vessel are sufficient to inoculate two culture mediums, this column indicates the number of vessels under testing
*3 For single-use products, the provisions for injectables in the upper part of the table apply.
Mycoplasma Testing


We are able to undertake the following three types of testing. Testing will be performed in accordance with the test methods stipulated in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia Reference Information.
-
Culture method
-
DNA staining method using indicator cells
-
Nucleic acids amplification test:NAT
Mycoplasma Testing
*1 Backed up samples are included.
*2 This indicates the period of time from the receipt of a sample to the issuance of the reports. An agreement must be signed and a procedure must be prepared in advance.
Test for mycoplasma growth inhibitory factors
The Japanese Pharmacopoeia states that "if the culture medium of cells under test contains mycoplasma growth inhibitory factors such as antibiotics, the growth inhibitory factors must be removed."
This test is performed prior to the culture method test, in principle.
Analytical method validation of mycoplasma testing(NAT)
The detection sensitivity and specificity are evaluated in the analytical validation.
Analytical Validation of mycoplasma testing
*1 Backed up samples are included.
*2 This indicates the period of time from the receipt of a sample to the issuance of the reports. An agreement must be signed and a procedure must be prepared in advance.
Detection sensitivity
To evaluate the detection sensitivity of NAT, seven mycoplasma species with known bacterial concentrations (CFU, etc.) are spiked into a cell suspension and evaluated.
Appropriate dilution series (e.g., 10 or 100.5 times dilutions) (minimum of three different dilution series) of the virus to be spiked are prepared, and multiple measurements are performed on different days.
For the main dilution series, measurement will be performed so that the total number of test repetitions is 24.
Bacteria species used
We demonstrate using the following seven species of bacteria listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia.
- ・Acholeplasma laidlawii
- ・Acholeplasma laidlawii
- ・Mycoplasma arginini
- ・Mycoplasma hyorhinis
- ・Mycoplasma orale
- ・Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- ・Mycoplasma salivarium
★Necessity of analytical validation of NAT
Most commercial kits have already been thoroughly validated by the manufacturer and the validity has been verified. If a different type or a different number of cells or if a different amount of samples are used in the test, however, the nucleic acid extraction efficiency and detection sensitivity may change, and sufficient detection sensitivity may not be obtained.
We report the results of this test after confirming the detection sensitivity of the sample under test. (The Japanese Pharmacopoeia also requires validation.)
Virus Testing (NAT)


The presence or absence of the following viruses in the samples under testing will be confirmed by nucleic acid amplification test (NAT).
Virus species to be confirmed: HBV, HCV, HIV-1, HTLV-1, B19V
*Please consult with us if you wish to confirm other than the above five species.
Virus Testing (NAT)
*1 X is determined by manufacturing scale, standard, and other factors (including backups).
*2 This indicates the period of time from the receipt of a sample to the issuance of the reports. An agreement must be signed and a procedure must be prepared in advance.
Validation test
The detection sensitivity and specificity are evaluated in the analytical validation.
Detection sensitivity
To evaluate the detection sensitivity of NAT, each virus (*) is spiked into a cell suspension and evaluated.
Appropriate dilution series (e.g., 10 or 100.5 times dilutions) (minimum of three different dilution series) of the virus to be spiked are prepared, and multiple measurements are performed on different days. For the main dilution series, measurement will be performed so that the total number of test repetitions is 24.
*Provirus for HTLV-1
In vitro virus test


Exogenous viruses will be detected using indicator cells (Vero, MRC-5, CHO-K1, and other cells).
In vitro virus test
Preliminary test
・Toxicity tests will be performed on three cell types.
・Interference tests will be performed for three virus types.
・A determination will be made by CPE (cytopathic effect).
Main test
・A determination will be made by CPE (cytopathic effect) and HAd (hemadsorption).
In vivo virus test
We inoculate adult mice, suckling mice, and embryonated eggs with samples, evaluate incidence and mortality, and detect exogenous viruses.
* This test will be performed by an outside institution that we have partnered with.
Antibody production test
Viruses are detected by inoculating mice (MAP), hamsters (HAP), and rats (RAP) with specimens, observing clinical signs, and confirming antibodies contained in the serum of the inoculated animals.
* This test will be performed by an outside institution that we have partnered with.
Other virus test
Virus detection tests will be performed using bovine-derived viruses (BT cells/Vero cells) and swine-derived viruses (PPK cells).
* This test will be performed by an outside institution that we have partnered with.