For quality tests as well, we offer our advanced chromosome analysis technology cultivated in clinical laboratory testing.
We undertake testing by the following methods.
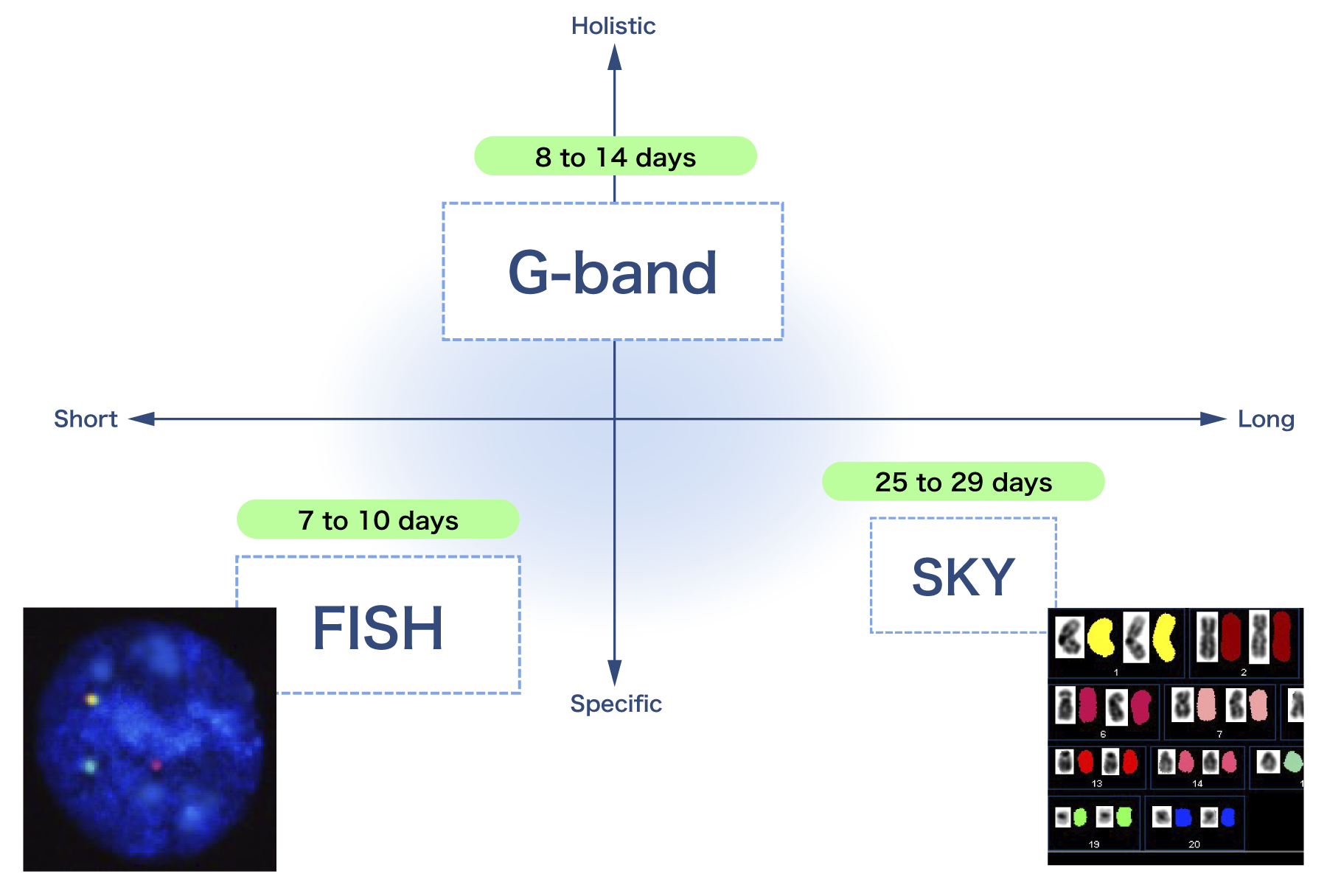
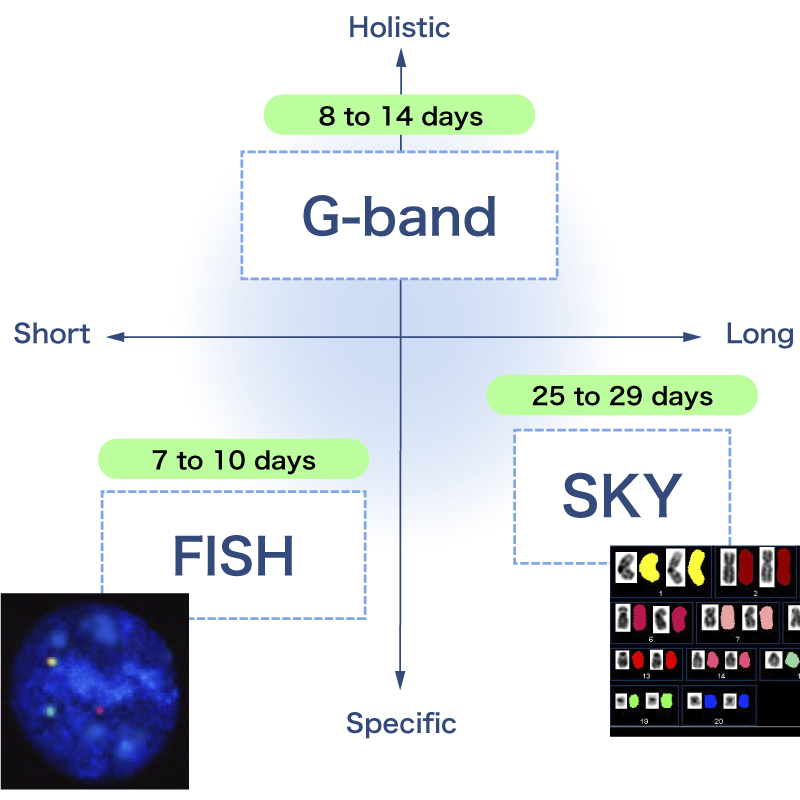
- G-band
- Detects numerical/structural anomalies
- Test method used most commonly
- FISH(Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization)
- Detects numerical anomalies
Detects structural anomalies (deletions, translocations) - Shorter test period compared to G-band
- SKY(Spectral Karyotyping)
- Auxiliary test for G-band
- Identifies chromosomes of unknown origin
Levels of chromosome and gene
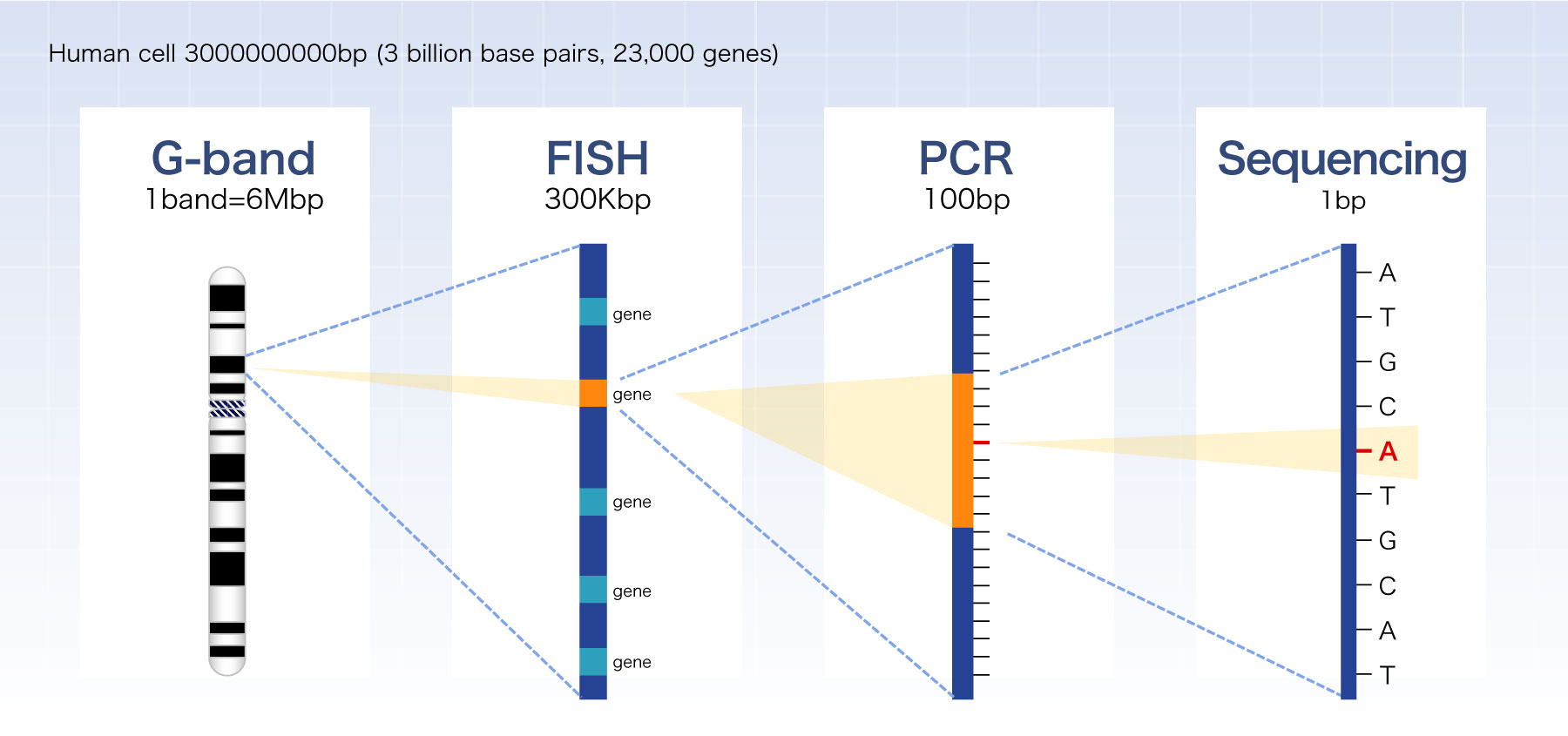
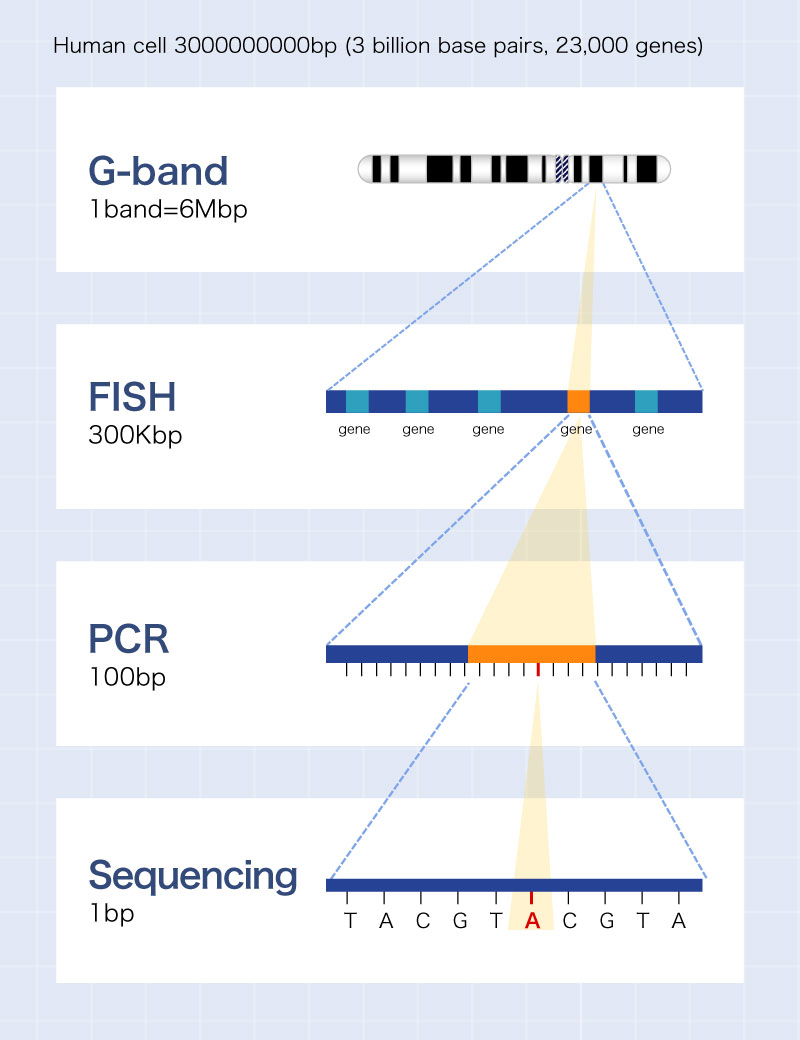
G-band
This is a morphological test in which juvenile cells from bone marrow fluid or blood are cultured, and the cell cycle is arrested in mid-mitosis, and stained differently for analysis after the addition of colcemid. colcemid.

■Features of the test
- ・Analyze various abnormalities on a single chromosome basis
- ・Analyze abnormalities on a cell-by-cell basis
- ・Able to assess the degree of progress of the abnormality
Most common test to detect chromosomal abnormalities
FISH
This is a test in which the target DNA in the interphase nucleus and the probe DNA labeled with a fluorescent dye are hybridized, and subsequently the fluorescent dye is colored at a specific wavelength and the signal pattern is detected under a fluorescence microscope.

■Features of the test
- ・In principle, 100 cells are used for testing while 20 cells are used for analysis in the G-band method
- ・The reporting time is shorter than the G-band method because testing can be performed without culture as interphases can be tested
- ・Test on a cell-by-cell basis
- ・Able to test specific probe DNA regions (genes)
Chromosome testing capable of gene level analysis
SKY
This is an analysis method that identifies individual chromosomes by combining 5 types of fluorescent dyes to stain 24 types of chromosomes in 24 fluorescent colors and reading the wavelength with a two-dimensional image spectroscopy system (SD-300) using an interferometer.

Advantages
- ・Able to identify structural abnormalities and marker chromosomes that are difficult to analyze using the G-band method
Disadvantages
- ・Difficult to detect structural abnormalities within the same type of chromosome, such as minute interstitial deletions and inversions
- ・May not be possible to detect translocations and insertions in minute areas
Testing that can identify chromosomes of unknown origin
Comparison of G-band, FISH and SKY
| G-band | FISH | SKY | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cells analyzed | Metaphase nucleus | Interphase nucleus | Metaphase nucleus |
| Detection limit | 14% | 5% | 45% |
| Number of cells analyzed | 20 cells | 100 cells | 5 cells |
| Target of detection | Chromosome | Nuclear DNA | Chromosomes (DNA) |
| Equipment used | Optical microscope | Fluorescence microscope | Fluorescence microscope |
| Features | Testing on a cell-by-cell basis | Testing of specific probe DNA regions (genes) | Testing on a cell-by-cell basis |
| Advantages | Analysis of all chromosomes | More cells analyzed compared to G-band method | Able to identify structural abnormalities and marker chromosomes that are difficult to analyze using the G-band method |
| Assess the degree of progress | Testing can be performed without culture as interphases can be tested | ||
| Able to be added from Carnoy's fixed cell | Able to be added from Carnoy's fixed cell | ||
| Easy to learn | |||
| Disadvantages | Possibility of poor proliferation | Possibility of false positive | Difficult to detect structural abnormalities within the same type of chromosome, such as minute interstitial deletions and inversions |
| Unable to detect minute abnormalities | Only the objective abnormalities | May not be possible to detect translocations and insertions in minute areas | |
| Take time to learn | Take time to learn | ||
| Test applications | Screening | Determination of related genes (definitive diagnosis) | Auxiliary test for G-band |
| Confirmation of the degree of progress | Monitoring |
| Cells analyzed | |
|---|---|
| G-band | Metaphase nucleus |
| FISH | Interphase nucleus |
| SKY | Metaphase nucleus |
| Detection limit | |
| G-band | 14% |
| FISH | 5% |
| SKY | 45% |
| Number of cells analyzed | |
| G-band | 20 cells |
| FISH | 100 cells |
| SKY | 5 cells |
| Target of detection | |
| G-band | Chromosome |
| FISH | Nuclear DNA |
| SKY | Chromosomes (DNA) |
| Equipment used | |
| G-band | Optical microscope |
| FISH | Fluorescence microscope |
| SKY | Fluorescence microscope |
| Features | |
| G-band | Testing on a cell-by-cell basis |
| FISH | Testing of specific probe DNA regions (genes) |
| SKY | Testing on a cell-by-cell basis |
| Advantages | |
| G-band | ・Analysis of all chromosomes ・Assess the degree of progress |
| FISH | ・More cells analyzed compared to G-band method ・Testing can be performed without culture as interphases can be tested ・Able to be added from Carnoy's fixed cell ・Easy to learn |
| SKY | ・Able to identify structural abnormalities and marker chromosomes that are difficult to analyze using the G-band method ・Able to be added from Carnoy's fixed cell |
| Disadvantages | |
| G-band | ・Possibility of poor proliferation ・Unable to detect minute abnormalities ・Take time to learn |
| FISH | ・Possibility of false positive ・Only the objective abnormalities |
| SKY | ・Difficult to detect structural abnormalities within the same type of chromosome, such as minute interstitial deletions and inversions ・May not be possible to detect translocations and insertions in minute areas ・Take time to learn |
| Test applications | |
| G-band | ・Screening ・Confirmation of the degree of progress |
| FISH | ・Determination of related genes (definitive diagnosis) ・Monitoring |
| SKY | ・Auxiliary test for G-band |